Ancient medicine was typically more holistic than our current medical practices, as they dwelled on the belief that healing is most effective when considering the whole person and each individual, rather than focusing on specific treatments for diagnosing specific diseases. Socrates, a Greek philosopher once said, “the part can never be well unless the whole is well.”
Surgeries
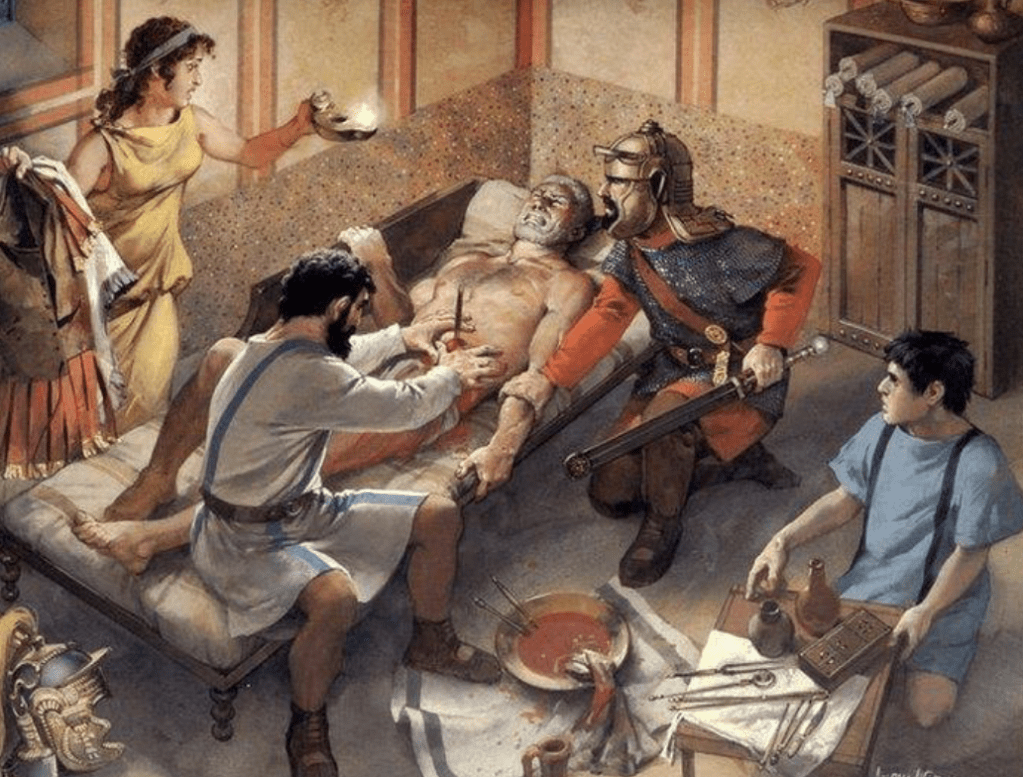
In Ancient societies, surgery was a rare practice, as there was a large uncertainty for life or death. It was often a fatal event. In order to perform these procedures, tools like a specula, bone lever, osteotomes, phlebotomist, probes, and bone drills were used. Anesthesia was also, obviously, not a viable option for Romans to use as a pain reliever during surgical procedures. Instead, opium and scopolamine were used. This early drug use is speculated to have been found at the bottom of Lakes where poppy seeds are found.
Herbal Remedies
Because of the limited knowledge and resources in Ancient Greek and Rome, doctors became expert herbalists and resorted to many natural remedies. They believed that nature trumped superstition at healing illness and disease. Hippocrates, a Greek physician, developed the theory of the four humors: blood, yellow bile, black bild, and phlegm. Following his theory, doctors tried to balance the four humors by making sure all things were right. In an attempt to balance the natural temperature of a patient, they kept a patient warm when they had a cold, kept feverish and sweaty patients dry and cool, bleed patients to restore the blood balance, and purged a person to restore the bile balance. Some of the ancient remedies include Birthwort, used to assist in childbirth; liquorice, used to calm the stomach, chest, liver, and kidney; and aloe to heal wounds. Some more common herbs that are still used today include basil, garlic (good for the heart), mint, and thyme. For nausea, the Romans believed that one of the cures was a three finger pinch of cumin to work wonders and relieve the irritation.
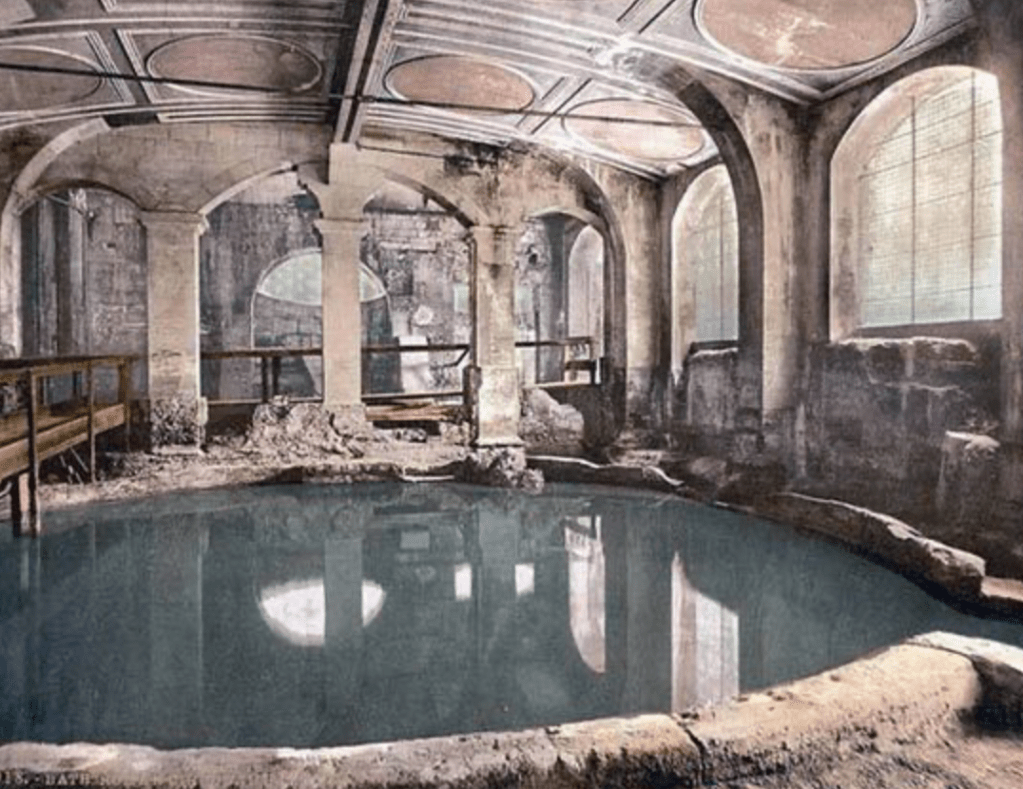
Thermal Baths and Springs
Thermal springs and baths were a common practice in both ancient Greece and Rome, where they turned the thermal baths for both religious and medical purposes. The thermal springs were a place of worship for Ascelepius, the god of medicine and healing, and the Nymphs. Hot and cold treatments were combined together for relieving muscular aches and pains as well as improving the body metabolism

Fun Facts:
- Urine Mouthwash: In particular areas, people used urine as mouthwash, which they preached for its whitening effects. A quote from a Roman poem states, “The fact that your teeth are so polished just shows you’re more full of piss.”
- The blood and liver of slain gladiators were believed to be cures for epilepsy. Roman doctors did not even have a real scientific understanding of the cause of epilepsy, but they did recommend drinking warm blood from a slain gladiator as a solution.
- When making diagnoses for patients, doctors also considered dreams. They believed that dreams could be signals from the soul about humoral imbalances in the body.
Leave a comment